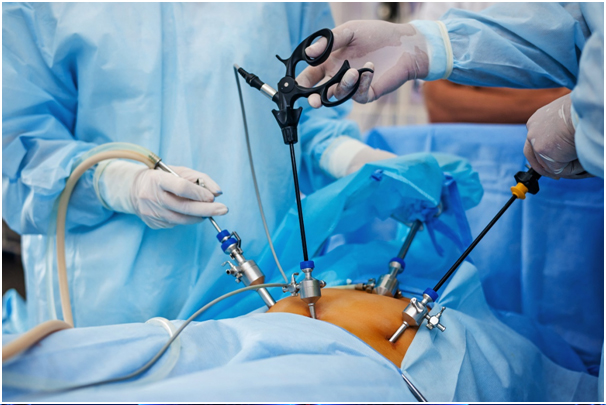
Laparoscopy, also known as diagnostic laparoscopy, is a surgical diagnostic procedure used to examine the organs inside the abdomen. It's a low-risk, minimally invasive procedure that requires only small incisions. Laparoscopy uses an instrument called a laparoscope to look at the abdominal organs. A laparoscope is a long, thin tube with high-intensity light and a high-resolution camera at the front. The instrument is inserted through an incision in the abdominal wall. As it moves along, the camera sends images to a video monitor.
Laparoscopy is often used to identify and diagnose the source of pelvic or abdominal pain. It's usually performed when noninvasive methods are unable to help with diagnosis.
Laparoscopy is performed when these tests don't provide enough information or insight for a diagnosis. The procedure may also be used to take a biopsy, or sample of tissue, from a particular organ in the abdomen.